Wondering what’s round trip time and what’s its impact on performance? This article will cover everything you need to know about the round trip time (RTT), how it’s calculated, what affects it the most, and how a CDN can help to decrease it.
What’s Round Trip Time?
Round trip time (RTT) measures the time it takes for the data to leave a starting point (the browser) and return to that very same point in milliseconds. It is a key metric used to measure network latency, page loading times, and the overall quality of a network.
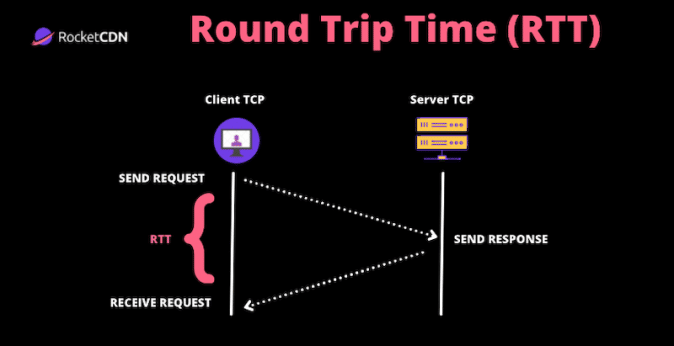
- RTT = The time taken for a small packet of data to travel across the network and return at the same point.
- Network latency = The communication delays over a network between the server and the user. Read our complete guide about network latency and how to reduce it with a CDN.
How To Calculate Round Trip Time (RTT)
Round trip time is the average server round-trip time plus the average round trip to the final client.
When a user requests page content on Chrome, a request is sent to the server to load that page. This request/response scheme takes time, and those “lags” are called “propagation delays”. Two propagation delays constitute one round trip time.
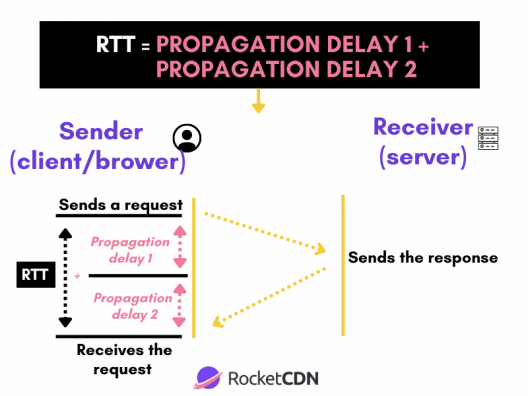
When it comes to the actual calculation, there is one simple formula to remember.
How to Fix an RTT Average
If you want to fix an RTT average, you should aim at improving the propagation delay time on both the browser and server sides.
To calculate the total RTT average, it’s crucial to know your client’s average server RTT and Average Client RTT.
Let’s break down the process into two simple steps.
Step 1: the calculation needs to be done on the server and client sides:
- Average Server RTT = (RTTs1 + RTTs2)/2
- Average Client RTT = (RTTc1 + RTTc2)/2
Step 2: then you have all the data to calculate the average total RTT
Average Total RTT = avRTTs + avRTTc
What’s a Good Round Trip Time?
A good round trip time (RTT) should be below 100 milliseconds for optimal performance. Anything above may affect the connection depending on the application.
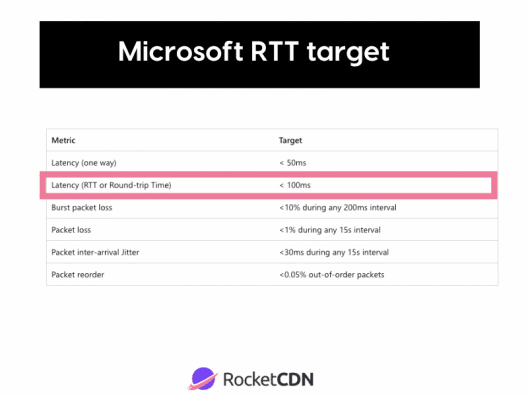
Example of a Round Trip Time at Microsoft
Microsoft has guidelines and rules to maintain healthy network quality. They published their network Performance requirements from a Skype for Business client to Microsoft network Edge. Here are the performance target requirements for optimal Skype for Business media quality.
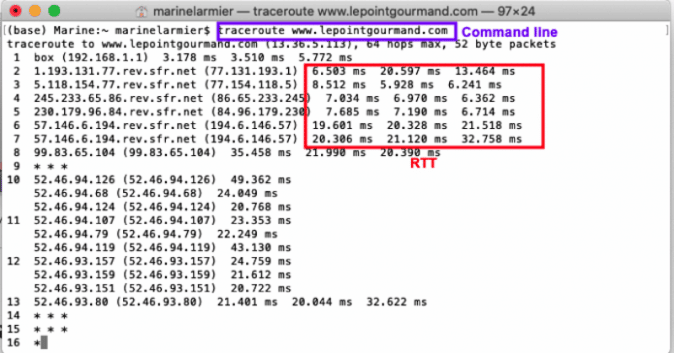
How to Check My Round Trip Time – Example
Round trip time can be seen thanks to a “ping” via the terminal command of your computer. Follow the steps below to launch the command line:
- Open your “Terminal Command” (on Mac) or your “CMD terminal” (on Windows)
- Type “traceroute” and “yourdomain” (it also works with your IP address)
- Press “Enter”
The round-trip times (RTTs) are expressed in ms from the third to the fifth column:
How Does Round Trip Time Work?
Round trip time is based on two main parameters:
- It determines the speed at which a network can operate as well as its global reliability.
- It allows users and operators to identify how long a signal will take to complete data transmission.
What Affects Round Trip Time?
The common factors affecting Round trip time are traffic, physical distance from the user to the servers, the transmission medium, and the overall infrastructure components.
Let’s go over each factor that impacts RTT the most:
- Physical distance – the high distance between the user computer (starting point) and the server (ending point) can be responsible for a high RTT. The data transfer time will take longer if the server is located on the opposite side of the world.
- Response time of the origin server – measured with the Time to First Byte (TTFB) metric, it’s the amount of time it takes a server to process and respond to a request. If a server is attacked with thousands of simultaneous requests (e.g, during a DDoS attack), its ability to respond efficiently will be compromised, resulting in a high RTT.
- Transmission medium – Connections are made via cables, satellite, wireless or optical fiber. Each way affects the connection speed differently.
- Local area network (LAN) traffic – if a local area is already overloaded, it can impact the connection before it reaches the public internet.
- Node count and congestion – the connection route may encounter some issues or congestion and may be redirected several times to intermediate nodes. The more nodes are touched, the slower the connection will result in a high RTT.
What’s the Impact of RTT on Performance and How a CDN Can Help
If the RTT is too high, time-outs and performance issues are very likely to occur. The Core Web Vitals of your website will also be impacted, resulting in a poor user experience.
Let’s take the example of the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures when the page starts loading the largest text block or image rendered on the screen. To ensure that the resource starts downloading as soon as possible, you should reduce the distance from the browser to the server.
This is exactly the purpose of a CDN: making the content available closer to visitors.
Let’s have a closer look at the four main reasons why a CDN can help reduce the RTT and improve performance:
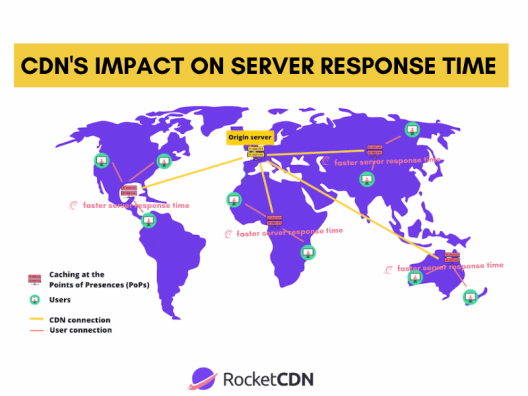
- CDNs decrease RTT because the users’ requests are handled by a local PoP and not the origin server, reducing the physical distance between a server and a user. CDN pops shorten the distance and improve the availability of assets, leading to an enhanced RTT.
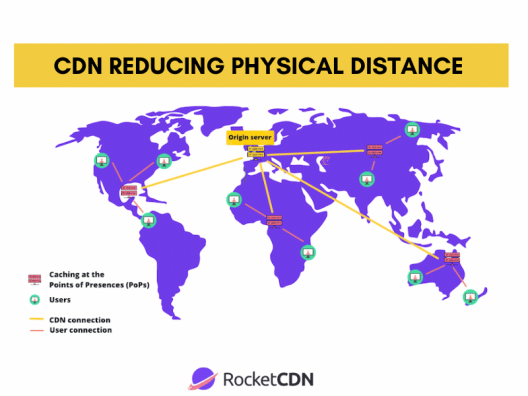
- A CDN reduces data transfer time between the cache servers and the user’s device by using caching to improve page load times. The idea is to get faster page loads for users located far away from the servers.
| Pro-tip for advanced caching: In addition to a CDN, you can also use WP Rocket, one of the best cache plugins for WordPress. |
- CDN helps to reduce server response time and the TTFB Time to First Byte (TTFB) metric. TTFB is the amount of time it takes for the server to get a response ready and the best way to reduce TTFB is by using a CDN to cache content. Kinsta run a performance audit before and after using a CDN, and they saw two interesting results: a faster loading site and less waiting time (TTFB).
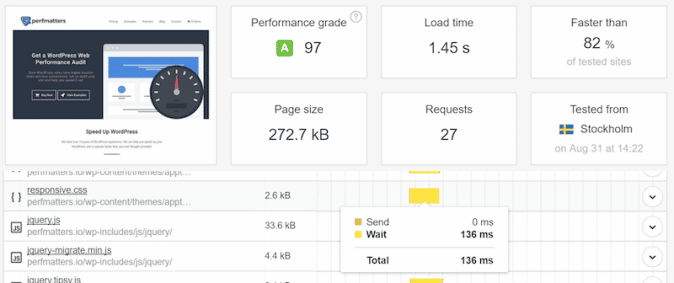
Scenario #1 – Performance results – No CDN
- Loading time = 1,45 s
- TTFB (wait time) = 136 ms
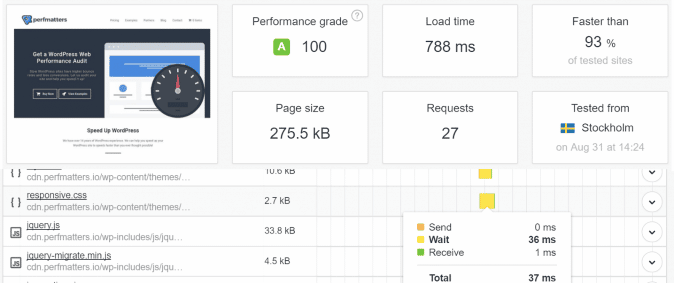
Scenario #2 – Performance results – With a CDN
- Loading time = 788 ms
- TTFB (wait time) = 36 ms
- Lastly, CDNs protect your origin server in case of DDoS attacks. If your website targets an attack, a CDN will help to ensure it doesn’t reach the origin server and render your site completely offline. Thanks to the CDN, the traffic will simply be redirected to other PoPs servers, and this will help maintain a good RTT.
Using RocketCDN to Reduce RTT
RocketCDN is a powerful CDN that uses caching and more than 35 Points of Presence to distribute the data around the globe, ensuring your website a low RTT. It’s also very simple and easy to use – RocketCDN does all the advanced settings for you.
Sounds promising?
Let’s go over the best features of RocketCDN that will help boost your performance and keep your RTT below 100 ms.
✅ RocketCDN: maintain a low RTT and TTFB but a high uptime
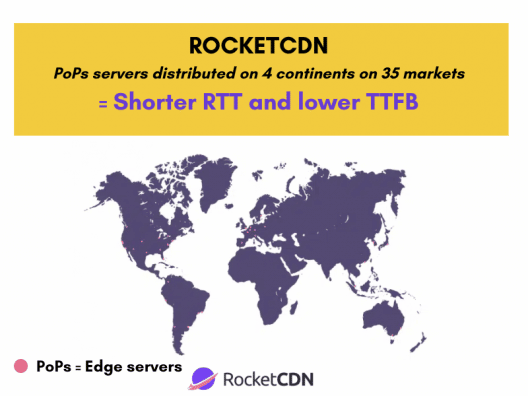
Present in more than 35 markets and on four continents, RocketCDN is a powerful CDN that helps reduce RTT and TTFB. The CDN ensures fast responsiveness for all international visitors located around the globe. Nobody wants any latency to occur, and a fast website is the key to a great user experience.
✅ Decrease the server response time with powerful caching
RocketCDN uses caching to make the content available faster for international users via PoPs, resulting in a faster server response time and increased performance.
✅ Network security and DDoS attacks protection
RocketCDN includes Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) traffic and protects your origin server in case of DDoS attacks. If your website is targeted, RocketCDN will ensure that it doesn’t reach the origin server. Visitors won’t experience any downtime. They will simply be redirected to the other edge servers. And most importantly, the RTT will not be impacted!
✅ Straightforward installation and compatibility with any website technology
RocketCDN works with any website technology making it easy to connect to any CMS, including WordPress or Joomla. There is a WordPress plugin that automatically points your assets to RocketCDN.

✅ Unlimited bandwidth and high scalability
RocketCDN can easily handle many visitors and unexpected traffic peaks with unlimited bandwidth. This is great for reducing the round trip time and avoiding any “hops” in the connection.
✅ A Cache Hit Ratio > 90%
With a Cache Hit Ratio superior to 90%, it’s safe to say that the data is properly cached and that RocketCDN can process many requests successfully. Like RTT, Cache Hit Ratio is also an important performance metric for a CDN.
Managing your Round trip time is straightforward with RocketCDN!
Using RocketCDN allows you to distribute content more efficiently worldwide, save on RTT, TTFB and increase the performance of your website. RocketCDN does all the heavy lifting for you – you don’t need to worry about the technical settings! On top of that, you have up to 48 hours to cancel it if you don’t see any improvements. Try RocketCDN and start reducing your round-trip time today!
